
AI risk assessments for construction: fast, compliant RAMS workflow you can trust
Jump To...

Site supervisor reviewing an AI-assisted risk assessment on a tablet
Who this is for
- Small to mid-sized UK contractors who want RAMS done in minutes, not hours.
- Site managers and RAMS authors who need a repeatable system their team will actually follow.
- Anyone being asked by clients for digital records, version control and proof that RAMS were briefed.
What this guide covers
- The exact steps to use AI for drafting risk assessments and method statements without falling foul of HSE or the Building Safety Regulator.
- Where human judgement is essential and how to record it.
- A ready-to-copy workflow that produces an audit trail, works offline on site, and slots into your existing document control.
HSE basics: the 5 steps and what still needs a human
HSE’s foundations don’t change when you use AI. The 5 steps are:
- Identify the hazards
- Decide who might be harmed and how
- Evaluate the risks and decide on precautions
- Record significant findings
- Review your assessment and update if needed
See HSE guidance on risk assessment, work at height, dust under COSHH, manual handling, vibration and protecting the public for trade-specific controls. Useful starting points: HSE risk assessment overview, work at height, construction dust, manual handling, vibration, protecting the public, and fire safety. The hierarchy of controls still applies; PPE is the last resort.
What still needs a human
- Site-specific hazards, controls and sequences. AI can draft generic wording; you must tailor to the exact site conditions, equipment, suppliers’ instructions and programme.
- Validating controls against UK guidance and manufacturer data.
- Briefing the team and checking understanding.
AI RAMS in practice: a simple, auditable workflow
Use this flow on every job. It’s fast, consistent and leaves a usable audit trail.
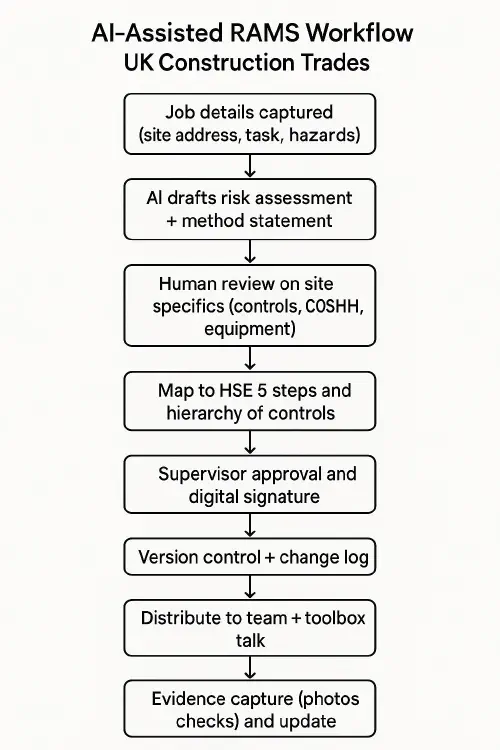
Flowchart showing an AI-assisted RAMS process from capture to golden thread storage
- Capture job details
- Use a structured intake form: site address, task, plant/tools, materials/chemicals, nearby services/public, access/egress, weather, permits, welfare. Photos help.
- Draft with AI
- Feed the form data to your chosen tool to produce a first draft of the risk assessment and method statement. Ask for controls mapped to HSE topics and the hierarchy of controls, and include emergency arrangements.
- Human review and tailoring
- Add site-specifics: exact access route, scaffold tags, MEWP type, COSHH assessments, manufacturer instructions, isolation points, rescue plan, waste disposal.
- Remove anything not relevant. Vague boilerplate is a red flag in inspections.
- Map to HSE topics and record decisions
- Cross-check against the 5 steps and applicable HSE topics linked above. Note what you accepted/changed and why. These notes belong in your change log.
- Approve and sign
- Supervisor approval with a digital signature. Capture version number, approver name, date and time.
- Brief the team
- Toolbox talk on the RAMS. Record attendees’ names/signatures. Attach photos of the briefing or a short video if useful.
- Evidence and updates
- During the job, capture evidence: pre-use checks, tagged scaffolds, dust control in place, hot works permits closed. Update RAMS if conditions change and bump the version number.
- File and share
- Store the signed RAMS, briefing record and evidence in your job folder. Share a view-only link or PDF to the client when requested.
Golden thread alignment on HRB projects
If you work on higher-risk buildings in England, you’ll be asked how your RAMS and evidence plug into the golden thread under the Building Safety Act.
- Use the client’s electronic facility to keep your RAMS and evidence current, versioned and readable. The principal contractor is responsible for maintaining the Construction Control Plan and Change Control Log; RAMS and their updates feed these. See GOV.UK guidance on the golden thread, Gateway 2 submission docs and completion requirements.
- Treat any change to agreed documents as controlled change. Update the change log and, where required, notify/seek approval before proceeding. See GOV.UK on change control and notifiable changes.
- Run a mandatory occurrence reporting system and brief your team on what to report. See GOV.UK MOR guidance.
Note: Dutyholder and competence duties under the Building Regulations apply to all work, not just HRBs. See The Building Regulations etc. (Amendment) (England) Regulations 2023.
Tooling: e-signatures, storage and evidence
- E-signatures: DocuSign, Adobe Sign or Dropbox Sign provide legally valid electronic signatures in the UK. Capture signer name, time, IP and document hash for your audit trail.
- Storage and sharing: Use structured job folders in Google Drive, SharePoint or your CDE. Use view-only links for clients to avoid uncontrolled copies.
- Evidence capture: Standardise photo naming and location tagging. Keep inspection logs, permits and test certs in the same folder as the RAMS.
- Version control: Include a version number, date, author, approver and a short change description on the title page. Keep a separate change log text file or sheet.
Common pitfalls and how to avoid them
- Generic boilerplate: If AI outputs vague controls, re‑prompt with specifics and UK references. Remove anything that doesn’t apply.
- No site specifics: Walk the site before approval. Add local hazards and exact control measures.
- Missing evidence: If you did it, prove it. Photos, permits, inspection sheets.
- Poor briefings: RAMS are only useful if the team understands them. Keep it short, use photos, and log attendance.
- No change control: If conditions change, update the RAMS and version number. Record what changed and why.
Related articles
- Health and safety file: what to include and a simple digital workflow that builds itself
- Method statement template for small works and maintenance: free example and how to brief your team
- Construction site safety audit checklist: digitise it, assign actions and prove compliance
FAQs
Is an AI-generated RAMS legal in the UK?
Yes, provided a competent person produces or validates it, it follows HSE’s 5 steps and is suitable and sufficient for the actual work. AI can draft; humans must tailor and approve.
Do we need digital signatures?
Digital signatures are widely accepted and help with audit trails. Make sure the signed PDF or record clearly shows who signed, when, and which version.
How do we brief non‑English speakers?
Provide translated summaries and pictograms and check understanding. See our guide on translating RAMS and site inductions safely with AI.
Will this satisfy the Building Safety Regulator on HRBs?
RAMS are one part of the picture. Ensure they link to your Construction Control Plan, Change Control Plan and MOR system, and that your evidence matches the agreed documents.
What should the AI prompt include?
Task, location, plant/tools, materials/chemicals, nearby services/public, access/egress, weather, permits, emergency plan, and ask for controls mapped to the hierarchy of controls and relevant HSE topics.
Want to slash training times and increase revenue per Engineer? Join our Waitlist: https://trainar.ai/waitlist
Ready to Transform Your Business?
Turn every engineer into your best engineer and solve recruitment bottlenecks
Join the TrainAR Waitlist