
Scaffold inspection checklist: UK legal requirements, 7 day rule and QR tag setup
Jump To...

Site supervisor scanning a QR-coded scaffold tag during inspection
Quick answer
- Scaffolds must be inspected:
- Before first use on site
- At least every 7 days while in use
- After events that could affect stability, like high winds, substantial alteration, impact or damage
- Keep a written report on or near the scaffold and retain it for 3 months after the work finishes.
- A visible tag system is not a legal requirement, but HSE expects inspections to be recorded and readily available to users. A tag plus QR code to a digital report is good practice.
References: HSE Scaffolds overview and HSE scaffold FAQs.
Who is competent to inspect
- Inspections must be carried out by a competent person. In practice this means someone with the right training, knowledge and experience for the type of scaffold.
- For system scaffolds, inspectors should have training specific to that system. See CITB/CISRS Scaffolding Inspection Training Scheme.
- On small jobs where you hire scaffold from a contractor, it’s still the user/hirer’s responsibility to ensure inspections happen and are recorded. You can contract a specialist to do them, but you keep the legal duty.
What to check: a practical list
Use this in your weekly and post-event inspections. Document findings and actions.
- Foundations and support
- Ground bearing capacity, sole boards and base plates set and not sinking
- No undermining by excavation, flooding or washout
- Standards, ledgers, transoms
- Plumb, level and securely connected; no missing components; no excessive corrosion or damage
- Bracing and ties
- Façade ties/brackets to design or TG20 guidance; frequency and pattern; no loose or missing ties
- Plan bracing and ledger bracing installed per design
- Platforms and edge protection
- Fully boarded working platforms; no large gaps; boards in good condition and secured
- Guardrails and midrails at correct heights; toe boards fitted where needed
- Access and egress
- Ladders or stair towers fixed and extending to safe handhold; no damaged rungs; trapdoors self-closing
- Loading and signage
- Load classes to design; loading bays and hop-ups installed to spec; SWL signs present and legible
- Protection of the public
- Debris netting, brickguards, fans, toe boards near public areas; exclusion zones where necessary
- Electrical and environmental
- Safe clearance from overhead lines; check wind exposure and sheeting attachments
- Modifications
- Any alterations recorded and re-inspected before use resumes
- Handover status and tagging
- Handover certificate on first use; visible tag updated with date, inspector and next due date
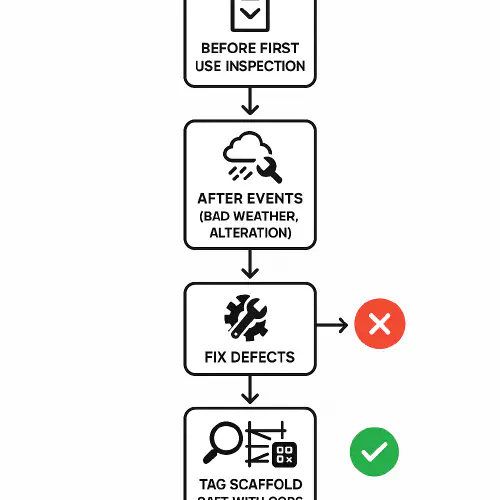
Scaffold inspection workflow diagram
Tag systems, records and QR codes
- Tag systems: HSE doesn’t mandate a particular tag, but a clear, visible status helps users. The key is having a written report available and up to date.
- Retention: Keep inspection reports on site (digital or paper) and for 3 months after work finishes.
- Simple QR-code setup you can deploy this afternoon:
- Create a Google Form or Microsoft Forms with fields matching the template below.
- Set the confirmation page to show a PDF link of the submitted report in your Drive/SharePoint folder.
- Generate a QR code that links to a live register or the latest report for that scaffold bay/tower.
- Print and laminate the QR next to your scaffold tag. Train supervisors to scan and check the date before stepping on.
- If you already use a job or asset app, create a “Scaffold” asset per job, attach inspection checklists, and print the asset’s QR code as your tag. This gives you an audit trail and expiry reminders.
Related Academy guides:
- QR-code inductions and access control: How to set up QR code site induction and CSCS Smart Check that records checks
- Reporting hazards: Near miss reporting on construction sites: simple steps, examples and a QR code setup
Tower scaffolds: extra points
Mobile towers bring different risks. Apply PASMA-style good practice:
- Pre-use checks each shift by the user plus formal weekly inspections
- Lock castors before use; remove or lock ladders when unattended
- Don’t move towers with people or loose materials on the platform
- Respect maximum wind speeds; add ballast if specified; check stabilisers/outriggers are fitted to design
Helpful background: HSE Scaffolds overview.
Scaffolding over highways
If your scaffold encroaches over a pavement or highway, you need a licence from the local council under the Highways Act. Expect conditions on lighting, protection fans and timing.
- Summary: GOV.UK scaffolding rules
Common mistakes to avoid
- Skipping the re-inspection after high winds or alterations
- Missing or improvised ties leading to sway
- Mixing components from incompatible systems
- No documented handover on first use
- Tag shows in-date, but report not available to operatives
Simple inspection report template
Copy these fields into your form or app. Save as PDF after each inspection.
Project: [Site name and address]
Principal contractor: [Company]
Scaffold location/ID: [Grid or bay ID]
Scaffold type/system: [Tube and fitting / System (make/model)]
Design reference: [TG20 compliance sheet or bespoke design number]
Inspector name and competency: [Name, role, training]
Inspection date/time: [dd/mm/yyyy hh:mm]
Next inspection due: [dd/mm/yyyy]
Checks (tick/notes):
- Foundations/sole boards/base plates
- Standards/ledgers/transoms
- Bracing and ties to design/TG20
- Platforms boarded and secured
- Guardrails/midrails/toe boards
- Access ladders/stair tower
- Loading bays/hop-ups to spec
- Signage/SWL displayed
- Protection to public (nets/brickguards/fans)
- Services/overhead lines clearance
- Sheeting/netting secure
- Alterations since last inspection
- Defects found (list)
- Actions taken / area isolated
Scaffold status: [Safe to use / Not safe – do not use]
Signature: [Inspector]
Handover certificate attached: [Yes/No]
Video: NASC Scaffold Inspections and Handover Certificates
Useful links and further reading
- HSE: Scaffolds – requirements and guidance
- HSE FAQs: Scaffolding
- CITB/CISRS: Scaffolding Inspection Training Scheme
- GOV.UK: Scaffolding rules
FAQ
How often should a scaffold be inspected?
Before first use, at least every 7 days while in use, and after events that could affect stability (for example high winds or alterations).
Do I have to use a tag system?
No, tags are not mandated. You must complete and keep written inspection reports. A visible tag helps users and is considered good practice.
Who is responsible for the inspection if I hire scaffold?
The user/hirer is responsible for ensuring statutory inspections happen and for keeping the records, even if a specialist is contracted to carry them out.
What counts as a competent person?
Someone with appropriate training, knowledge and experience for the scaffold in question. For system scaffolds, training on that system is expected.
How long must I keep inspection reports?
Until the work is complete and for a further 3 months.
Ready to Transform Your Business?
Turn every engineer into your best engineer and solve recruitment bottlenecks
Join the TrainAR Waitlist